Electronic Fluorinated Fluids: The "Invisible Guardians" of the Tech Industry
—— Unveiling the Key Materials Behind Cutting-Edge Manufacturing
In today's era of rapid technological advancement, critical sectors such as precision semiconductor chip manufacturing, efficient heat dissipation in data center servers, and safety protection for new energy batteries all rely on a seemingly ordinary yet indispensable liquid—electronic fluorinated liquid. Acting as the "transparent lifeblood" of modern high-end manufacturing, it remains largely unseen by the public yet stands as a core material driving continuous upgrades in cutting-edge industries like 5G communications, artificial intelligence, and new energy.
I. What is Electronic Fluorinated Liquid?
Electronic fluorinated liquids are a class of functional liquid materials primarily composed of fluorocarbon compounds. Within their molecular structure, hydrogen atoms are highly substituted by fluorine atoms, forming exceptionally stable C-F bonds. This unique chemical structure endows them with outstanding chemical inertness, superior electrical insulation, excellent thermal stability, and remarkable heat dissipation capabilities. Its dielectric constant can be as low as 1.8–2.0 (for reference, air has a dielectric constant of 1), meaning it is virtually non-conductive. Its boiling point range spans a broad temperature spectrum from 35°C to 275°C, reaching up to 290°C under special conditions, enabling it to easily adapt to various extreme industrial environments.
Different Types of Perfluoropolyether(PFPE)
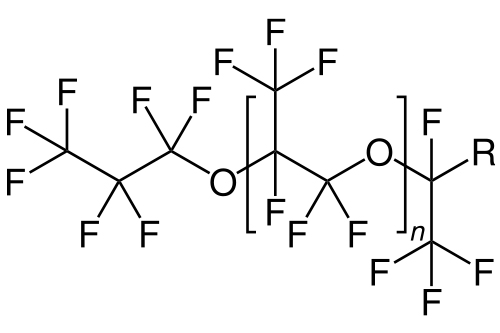 | 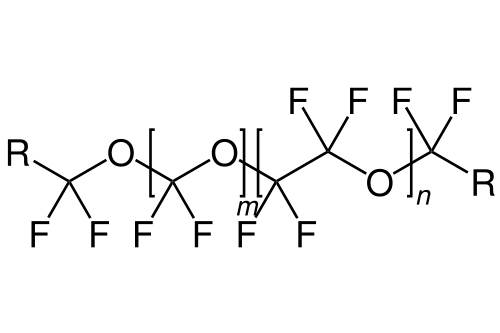 |
| PFPE-K | PFPE-Z |
II. The Four Core Application Areas of Electronic Fluorinated Fluids
1. The "Key Assistant" in Semiconductor Manufacturing
In the semiconductor manufacturing process, electronic fluorinated liquids play an indispensable role. They can be used to clean nanoscale impurities from wafer surfaces, effectively preventing corrosion to circuits that traditional solvents might cause. Moreover, certain fluorinated solutions, leveraging their high purity and low surface tension, are specifically employed for wafer cleaning. They utilize the Marangoni effect to remove moisture from wafer surfaces, thereby circumventing potential safety hazards associated with traditional isopropyl alcohol (IPA). This provides robust assurance for the high-precision stages of chip manufacturing.
2. The "Cooling Expert" of Data Centers
Currently, against the backdrop of carbon peaking and carbon neutrality, government departments are imposing increasingly stringent regulations on the energy efficiency (PUE) of data centers. The "Special Action Plan for Green and Low-Carbon Development of Data Centers," jointly issued by the National Development and Reform Commission and other departments on July 3, 2024, states: "By the end of 2025, the power usage effectiveness (PUE) of newly constructed and expanded large and hyperscale data centers must be reduced to below 1.25. For national hub node data center projects, the PUE must not exceed 1.2."
Simultaneously, the rapid advancement of AI technology has driven exponential growth in computing power demand. The widespread adoption of high-density GPU servers has caused data center energy consumption to surge dramatically, posing significant challenges to achieving PUE compliance. Against this backdrop, reducing cooling system energy consumption has become critical. According to ZTE's Liquid Cooling Technology White Paper, cooling systems account for over 24% of typical data center energy consumption—the largest share among auxiliary energy sources. Therefore, reducing cooling system energy consumption can significantly lower PUE. Data centers employing phase-change immersion liquid cooling technology can achieve a PUE of 1.15 to 1.05, delivering exceptional energy savings. The electronic fluorinated liquid plays a crucial cooling role in this process, enabling data centers to operate in a green and highly efficient manner.
Immersion Liquid-Cooled Servers
3. The "Insulation Guardian" for High-Voltage Power Equipment
In high-voltage applications such as ultra-high voltage transformers, new energy vehicle battery packs, and energy storage power stations, fluorinated liquids serve as insulating cooling media, ensuring long-term stable operation of equipment. For instance, KEY-140, an electronic fluorinated liquid under the KEY brand by Zhongke Weixin Materials, boasts a boiling point of 275°C and a breakdown voltage exceeding 40 kV/mm. This means it maintains stable properties even in high-temperature environments without decomposition or degradation, significantly reducing the risk of electrical faults like short circuits and safeguarding the safe operation of high-voltage power equipment.
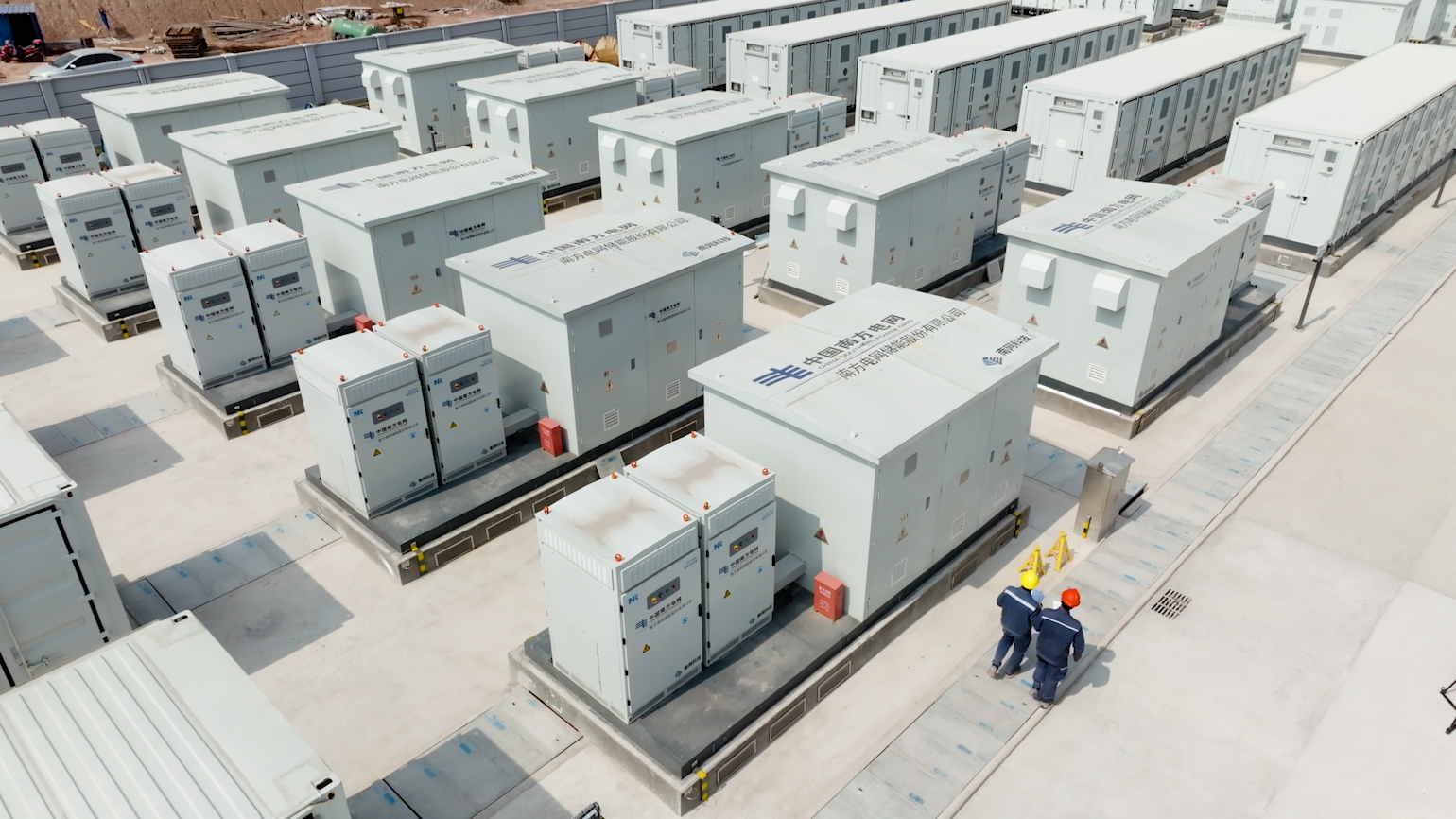
The world's first immersion liquid-cooled energy storage power station—China Southern Power Grid Meizhou Baohu Energy Storage Power Station
4. "Extreme Environment Adaptors" in Aerospace and Military Fields
With its unique physicochemical properties and exceptional tolerance to extreme temperatures (-130°C to 275°C), electronic fluorinated fluid finds extensive application in the cooling systems of fighter jet radars and satellite electronics. NASA's public reports demonstrate that fluorinated fluid exhibits distinct advantages and significant practical value in the demanding environments of spaceflight applications. It provides robust assurance for the reliable operation of aerospace and military equipment under extreme conditions.
III. Why Are Electronic Fluorinated Liquids Difficult to Replace?
1. Outstanding physicochemical properties
- Chemical Inertness: Electronic fluorinated fluids exhibit minimal chemical reactions with common substances such as acids, alkalis, and metals. Certified by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), they possess a LD50 (lethal dose 50) exceeding 5000 mg/kg, classifying them as practically non-toxic. This ensures stability in diverse complex application environments without introducing impurities or triggering adverse reactions.
- Superior Thermal Management: With a thermal conductivity of 0.06–0.12 W/(m·K)—significantly higher than air's 0.026 W/(m·K)—it dramatically enhances heat dissipation efficiency. This effectively addresses heat accumulation in electronic devices during operation, ensuring stable performance.
- Environmental Sustainability: The new hydrogen fluoride ether (HFE) fluorinated fluid has an Ozone Depletion Potential (ODP) of 0, fully complying with the environmental requirements of the Montreal Protocol. In the global trend of increasing emphasis on environmental protection, this characteristic endows it with long-term development potential and application prospects.
2. Rigid Demand Driven by Industrial Upgrading
With the advancement of the U.S. CHIPS and Science Act and the implementation of China's 14th Five-Year Plan for electronic materials development, achieving self-reliance and control in the semiconductor supply chain alongside the green transformation of data centers have become unstoppable global trends. According to statistics and forecasts from market research firm QYResearch (Hengzhou Bozhi), the global electronic fluorinated liquid market reached $1.38 billion in sales in 2024. It is projected to surpass $2 billion by 2031, reaching $2.127 billion, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.5% from 2025 to 2031. Given this market trajectory, the prospects are vast, underscoring its pivotal role in industrial upgrading and further highlighting its irreplaceable characteristics.
IV. Breakthroughs and Rise of Domestic Electronic Fluorinated Fluids
For a considerable period, the core technology of electronic fluorinated liquids has been monopolized by international giants like 3M. However, in recent years, Chinese technology companies have accelerated their independent R&D efforts, gradually breaking through foreign technological barriers and successfully overcoming this critical bottleneck. Take Zhongke Wei New Materials as an example. Its KEY series of electronic fluorinated liquids, including models KEY-114, KEY-117, KEY-118, and KEY-125, have all passed industry certification. They have achieved internationally advanced levels in key indicators such as purity, dielectric strength, thermal conductivity, boiling point, surface tension, and viscosity. These products have been successfully applied in multiple scenarios including new energy, lithium batteries, AI data centers, and semiconductor manufacturing. They have established a strong reputation in the domestic market for electronic fluorinated liquids, signifying a substantial breakthrough for China in this critical material sector and positioning the country to compete effectively in the global marketplace.
Closing Remarks: Small Liquid, Big Future
The value of electronic fluorinated liquids extends beyond their formidable technical barriers; it lies in their role as a bridge between materials science and advanced manufacturing. From the smartphones we use daily to the colossal supercomputers in data centers; from battery cooling systems in new energy vehicles to satellite electronics protection devices orbiting in space—this seemingly "invisible" liquid has become an indispensable enabler in modern technology industries. Looking ahead, as domestic production accelerates, electronic fluorinated liquids will undoubtedly play an increasingly vital role in high-end manufacturing, writing their own glorious chapter.
LATEST NEWS
- Using Electronic Fluorinated Fluids in Heat Pipes: What Makes Them Special? 2026-02-28 15:06:08
- Zhongke Micro New Materials (Shenzhen) Co., Ltd. Successfully Holds 2026 Annual Meeting: Tracing Our Journey of Striving, Charting a New Chapter of Development Together 2026-02-13 15:30:57
- Zhongke Micro New Materials has been recognized as a "Specialized, Refined, Distinctive, and Innovative" enterprise by Shenzhen Municipality, marking progress in its pursuit of high-end fluorine-silicon fine electronic chemicals 2026-02-13 16:46:47
- Evolution of Data Center Cooling Technologies: From Water Cooling to Emerging Solutions 2026-01-30 17:20:15
- From Server Racks to Battery Racks: Why Immersion Cooling Is the Future of Safe Energy Storage in Data Centers 2026-01-30 21:20:46
- Introduction to Immersion Cooling 2025-12-30 21:46:36
- Good News|Zhongke Micro New Materials Secures Third Place in the Industry Finals of the Longgang District Preliminary Round for the 17th China Shenzhen Innovation and Entrepreneurship Competition 2025-12-19 10:29:54
- Conquering the Summit of Wutong Mountain, Tempering the Spirit of Teamwork | Zhongke Micro New Materials' Autumn Team-Building Event at Wutong Mountain Concludes Successfully 2025-11-02 22:42:15
- Zhongke Micro KEY High-Performance Gas-Phase Welding Fluid: Unleashing the Full Potential of Gas-Phase Welding Technology 2025-08-07 14:46:00
- Zhongke Micro New Materials Recognized as National High-Tech Enterprise Innovation Engine Propels New Journey Toward Domestic Production of Fluorinated Materials 2025-03-19 17:54:11